The quest for energy-efficient solutions has gained the utmost importance in an era of fast-paced technological advancements and increasing emphasis on environmental sustainability. Innovations that minimize energy consumption and reduce carbon emissions have taken centre stage from automobiles to appliances. And now, the spotlight has shifted to an essential aspect of every home: the high-efficiency furnaces.

What are High-Efficiency Furnaces?
High-efficiency furnaces are one of the best HVAC system options specifically engineered to optimize energy efficiency and minimize energy loss in contrast to standard or traditional furnaces. They incorporate state-of-the-art technologies and innovative features that enable them to extract more heat from the fuel they utilize. As a result, they consume less energy, leading to decreased utility expenses.
Pros and Cons of High-Efficiency Furnaces
Here are some pros and cons of high-efficiency furnaces:
Pros of High-Efficiency Furnace Units
- Energy savings: High-efficiency furnaces are designed to extract more heat from the combustion process, which leads to greater energy efficiency. This means they can convert a significant portion of their consumed fuel into usable heat for your home. As a result, they can help lower your energy bills and reduce your carbon footprint.
- Reduced environmental impact: Due to their higher efficiency, high-efficiency furnaces produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to standard furnaces. This can contribute to a cleaner environment and help mitigate climate change.
- Improved indoor comfort: High-efficiency furnaces often come with variable-speed blowers, providing a more consistent and comfortable indoor temperature. These blowers can adjust their speed to match your home’s heating needs more precisely, resulting in fewer temperature fluctuations and improved air circulation.
- Better air quality: High-efficiency furnaces typically have advanced air filtration systems that can capture more airborne particles, such as dust, pollen, and allergens. This can improve indoor air quality and benefit individuals with allergies or respiratory conditions.
Cons:
- Higher upfront cost: High-efficiency furnaces generally have a higher initial purchase and installation cost than standard furnaces. The technology and components used in these furnaces are more advanced, contributing to the increased price tag. However, the long-term energy savings can help offset the initial investment.
- Complex installation and maintenance: High-efficiency furnaces require professional installation and regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. The condensing process produces acidic condensate, which needs proper drainage and disposal. Additionally, the furnace’s advanced components may require more frequent inspections and maintenance, potentially increasing the overall maintenance costs.
- Compatibility issues: High-efficiency furnaces may require specific venting systems to accommodate their condensing process. This could mean additional installation or modification costs, especially if your home’s existing venting infrastructure is incompatible with the new furnace.
- Potential moisture-related issues: The condensing process in high-efficiency furnaces produces water vapour as a byproduct. If not adequately drained or vented, this moisture can lead to mould growth or damage to the furnace. Adequate drainage and ventilation are essential to prevent these problems.

Furnace Efficiency Rating
Furnace efficiency rating measures how effectively a furnace converts fuel into heat.
It helps homeowners and professionals evaluate the energy efficiency of a furnace and compare different models to make informed decisions.
A higher efficiency rating indicates that a furnace can generate more heat while consuming less fuel, exemplifying greater efficiency.
There are two commonly used efficiency rating systems for furnaces:
- Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE)
- Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF).

Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE):
AFUE is the most commonly used rating system for furnaces in North America. It measures the percentage of fuel converted into usable heat over a typical year.
AFUE ratings typically range from 80% to 98.5% or even higher. Here’s a general breakdown of what these ratings typically signify:
- 80% AFUE: These are older, less efficient models commonly found in older homes. They convert 80% of the fuel into heat, while the remaining 20% is lost through exhaust gases.
- 90% AFUE: These are mid-range furnaces that offer good energy efficiency. They convert 90% of the fuel into heat, with 10% lost through exhaust gases.
- 95% AFUE and above: These high-efficiency furnaces are more expensive but offer significant energy savings. They convert 95% or more of the fuel into heat.
It’s important to note that AFUE ratings do not consider heat losses through the distribution system (ductwork) or other affecting overall heating efficiency.
Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF):
HSPF is specifically for heat pumps, which can provide heating and cooling. It measures the efficiency of the heating mode over an entire heating season. The higher the HSPF rating, the more efficient the heat pump is at heating. HSPF ratings typically range from 7 to 13 or higher.
When considering furnace efficiency ratings, it’s essential to consider factors such as climate, fuel costs, and the specific needs of your home. A higher efficiency rating may result in greater upfront costs, but it can lead to significant energy savings over the long term.
High-Efficiency Furnaces for Mobile Homes

Regarding high-efficiency furnaces for mobile homes, there are a few factors to consider due to the unique characteristics of mobile home heating systems. Here are some crucial points to keep in mind:
- Size and Venting: Mobile homes typically have limited space and specific venting requirements. High-efficiency furnaces designed for mobile homes are often compact and designed to fit within the available space. To ensure safe operation, they may also require specialized venting systems, such as direct venting or sealed combustion.
- AFUE Rating: Look for high-efficiency furnaces with a high AFUE rating. As mentioned earlier, a higher AFUE rating indicates better energy efficiency and can help you save on heating costs. Consider furnaces with AFUE ratings of 90% or higher for optimal efficiency.
- Compliance with HUD Standards: Mobile homes in Canada are subject to specific regulations set forth by the appropriate regulatory authorities. Ensuring that any furnace you select adheres to these standards to meet safety and quality requirements is crucial.
- Fuel Type: Determine the appropriate fuel type for your mobile home. Standard options include natural gas, propane, and electric furnaces. Consider availability, cost, and energy efficiency when selecting the fuel type for your high-efficiency furnace.
- Professional Installation: It is crucial to have a qualified HVAC professional install the high-efficiency furnace in your mobile home. They will ensure proper sizing, venting, and compliance with local codes and regulations.
When selecting a high-efficiency furnace for your mobile home, it’s advisable to consult with an HVAC specialist who has experience with mobile home heating systems. They can assess your requirements, recommend suitable models, and provide expert installation services to ensure efficient and safe operation.
High-Efficiency Vs. Mid Efficiency Furnaces
High-efficiency and mid-efficiency furnaces are heating systems commonly used in residential and commercial buildings. They differ primarily in their energy efficiency, cost, and environmental impact.
High-efficiency furnaces are designed to maximize energy savings.
With an AFUE rating of 90% or higher, these systems excel in extracting more significant heat from the fuel they consume, minimizing energy wastage during the combustion process.
Some high-efficiency furnaces even boast AFUE ratings as high as 98%, indicating that they convert 98% of the fuel into usable heat. This higher efficiency translates into lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills over time.
On the other hand, mid-efficiency furnaces have AFUE ratings ranging from 80% to 89%. While they are less efficient than their high-efficiency counterparts, they still offer better energy efficiency compared to older, less efficient furnaces. Mid-efficiency furnaces extract less heat from the fuel, resulting in a slightly higher energy waste during combustion. However, they can still provide reliable heating performance at a lower initial cost.
When considering the cost, it’s important to note that high-efficiency furnaces generally have a higher upfront price than mid-efficiency models.

Incorporating advanced technology and additional components, such as venting systems and condensate drain systems, primarily accounts for their exceptional efficiency.
However, the long-term cost savings associated with high-efficiency furnaces are worth considering. The reduced energy consumption can offset the initial investment, leading to lower overall operating costs throughout the furnace’s lifespan.
Mid-efficiency furnaces are more affordable to purchase and install. They have more specific venting requirements and do not require a condensate drain system. This can make them a more budget-friendly option for those looking for a furnace replacement or upgrade.
Regarding environmental impact, high-efficiency furnaces are the more eco-friendly choice—their improved energy efficiency results in lower greenhouse gas emissions.
By burning fuel more effectively and wasting less energy, high-efficiency furnaces contribute to reduced carbon dioxide emissions and help mitigate climate change.
While mid-efficiency furnaces are less environmentally friendly than their high-efficiency counterparts, they still produce fewer emissions than older, less efficient ones. Upgrading to a mid-efficiency furnace can be a step towards reducing your carbon footprint.
However, it may offer higher energy savings and environmental benefits than a high-efficiency model.
It’s also important to consider potential rebates and incentives when choosing between high-efficiency and mid-efficiency furnaces.
To encourage energy efficiency, numerous utility companies and government agencies provide incentives.
These incentives are often more common for high-efficiency furnaces as they prioritize the highest levels of energy savings. By taking advantage of rebates and incentives, you can offset some of the higher upfront costs associated with high-efficiency furnaces.
Best High-Efficiency Furnaces in the Market (Types)
There are three primary types of high-efficiency furnaces that you can choose for your home or commercial building.
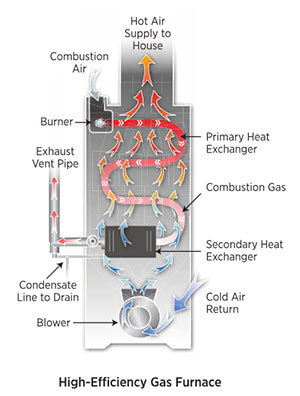
High-Efficiency Gas Furnaces
A high-efficiency gas furnace is precisely engineered to optimize energy efficiency and minimize energy consumption as a heating system.
Using natural gas or propane combustion, a high-efficiency gas furnace generates heat distributed throughout a building or residence. (But does a gas furnace work without electricity?)
Here’s how a high-efficiency gas furnace typically works:
- Ignition: The furnace is ignited using an electronic ignition system or a pilot light. The ignition source ignites the gas, creating a flame.
- Combustion: The gas flows into a combustion chamber, which mixes with air and is burned. This combustion process generates heat.
- Heat Exchanger: The heat produced by the burning gas is transferred to a heat exchanger, a metal component located inside the furnace. The heat exchanger absorbs the thermal energy from the combustion process.
- Air Circulation: As the heat exchanger gets hot, a blower fan forces air from the surrounding space over the hot surface of the heat exchanger. The air absorbs heat from the exchanger and becomes warm.
- Exhaust: The byproducts of combustion, including gases like carbon dioxide and water vapour, are expelled through a vent or chimney. Sure high-efficiency furnaces employ a secondary heat exchanger to extract extra heat from the exhaust gases before their discharge. This supplementary process significantly enhances the overall efficiency of the furnace.
- Distribution: The warmed air is then distributed through the ductwork of the building using a blower fan. The ducts deliver the heated air to different rooms or zones, providing warmth and comfort throughout the building.
- Control System: The furnace has a control system that monitors and regulates the heating process. It senses the temperature in the building and adjusts the operation of the furnace accordingly to maintain the desired temperature.
High-Efficiency Electric Furnaces
High-efficiency electric furnaces are heating systems that utilize electricity as their energy source to produce heat. While gas furnaces burn fuel, electric furnaces use electrical resistance elements to generate heat.
Here’s an overview of how high-efficiency electric furnaces work:
- Electric Heating Elements: Inside the electric furnace are one or more heating elements made of electrically resistant material, typically coils or strips. When an electric current passes through these elements, they heat up and emit thermal energy.
- Air Circulation: A blower fan forces air over the heated elements, causing the air to absorb the heat. The fan circulates the warmed air through the system and into the living spaces via ductwork.
- Control System: Like gas furnaces, electric furnaces have a control system that monitors and regulates the heating process. It includes temperature sensors that detect the temperature in the building and control the operation of the furnace to maintain the desired temperature.
- Distribution: The warm air is distributed throughout the building via the ductwork system, delivering heat to various rooms or zones.
Unlike gas furnaces, high-efficiency electric furnaces don’t produce combustion byproducts or require venting for exhaust gases. As a result, they are typically more compact, require less maintenance, and can be installed in a broader range of locations within a building. However, it’s important to note that electric furnaces generally have higher operating costs than gas furnaces, as electricity is typically more expensive than natural gas or propane.
Need HVAC systems for your homes? Check out the most affordable furnaces in Toronto.
High-Efficiency Furnace Cost
The price of a high-efficiency furnace can fluctuate based on various factors, including the brand, model, size, and any additional features it may have.
Additionally, installation costs can vary based on your location and the complexity of the installation process.
A high-efficiency furnace can range from $2,500 to $6,000 for the unit alone. This price range typically includes mid-range to higher-end models with an efficiency rating of 90% or above.
Remember that more advanced and energy-efficient models may be on the higher end of this price range.
Installation costs typically range from $1,500 to $3,500, depending on various factors, such as the complexity of the installation, the need for additional ductwork or modifications, and the labour rates in your area.
It’s important to note that these cost estimates are rough averages, and prices can vary significantly depending on the abovementioned factors. Obtaining quotes from multiple HVAC contractors in your area is recommended to get a more accurate estimate for your specific needs.
| Fuel Type | Furnace Type | Furnace Cost Range (USD) | Installation Cost Range (USD) |
| Gas | High-Efficiency | $1,500 – $4,000 | $2,500 – $6,000 |
| Electric | High-Efficiency | $1,000 – $3,000 | $1,500 – $4,000 |
| Propane | High-Efficiency | $1,800 – $4,500 | $2,500 – $6,500 |
If you’re among the homeowners perplexed by furnace prices, deciding whether to purchase or rent the system can be overwhelming. To assist you in making the right choice for your home or commercial building, we offer a comprehensive guide that clarifies whether to rent or buy furnaces.
How Many Watts Does High-Efficiency Furnace Use?
- Gas Furnace: High-efficiency gas furnaces typically use a range of 90,000 to 150,000 BTU (British Thermal Units) per hour. You can use the conversion factor of 1 BTU/hour = 0.29307107 watts to convert BTU to watts. Therefore, a high-efficiency gas furnace can consume approximately 26,407 to 43,965 watts.
- Electric Furnace: Electric furnaces are powered by electricity and do not rely on combustion like gas. The power consumption of electric furnaces is measured in kilowatts (kW). The wattage rating of electric furnaces can vary depending on their size and heating capacity. On average, electric furnaces range from 10 kW to 20 kW. Remember that this is the power consumed by the furnace itself, and the overall power usage will depend on the specific heating requirements and usage patterns.
- Propane Furnace: The power consumption of a propane furnace can range from around 40,000 BTU/h to 120,000 BTU/h or more. Converting this to watts, the power consumption would be approximately 11,724 to 35,128.
